When driving on highways at night, visiting a large sports stadium, or passing through an industrial complex after dark, you’ve likely benefited from bright, widespread illumination that turns night into day. This type of lighting often comes from tall structures standing high above the ground, casting light over large areas. These structures are known as high mast lights, and they play a critical role in ensuring safety, productivity, and visibility in various large-scale environments. This guide explains what a high mast light is, how it works, its key components, and the diverse settings where it is most effectively used.
What Is a High Mast Light?
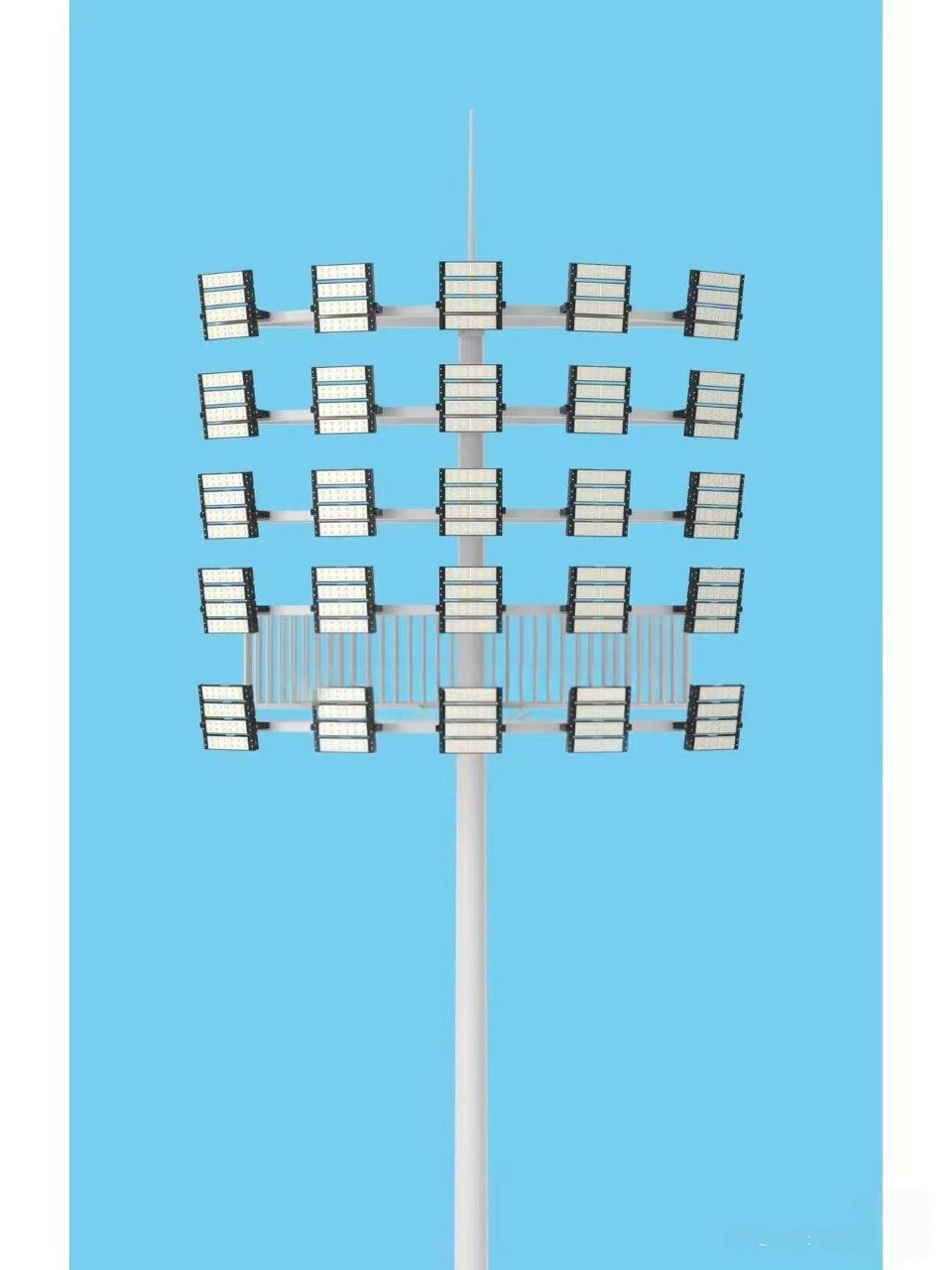
A high mast light is a tall lighting system designed to provide bright, uniform illumination over large areas. Unlike standard streetlights or floodlights mounted on short poles (typically 10–20 feet tall), a high mast light is installed on a tall mast, ranging from 60 feet (18 meters) to over 150 feet (45 meters) in height. This elevated position allows the light to spread over a much wider area, making it ideal for lighting large spaces that require consistent brightness across their entire expanse.
A typical high mast light system consists of a sturdy mast (usually made of steel), multiple light fixtures mounted on a circular or rectangular frame at the top, and a base structure to anchor the mast securely to the ground. Many high mast light systems also include a maintenance mechanism, such as a winch or hydraulic lift, that lowers the light fixture assembly to ground level for easier bulb replacement, cleaning, or repairs—eliminating the need for expensive cherry pickers or cranes.
The light fixtures themselves have evolved over time, with modern high mast light systems now predominantly using energy-efficient LED technology. Older systems often used metal halide or high-pressure sodium bulbs, but LEDs offer longer lifespans, lower energy consumption, and better light quality, making them the preferred choice for new high mast light installations.
Key Components of a High Mast Light System
A high mast light system is more than just a tall pole with lights—it’s a complex structure designed for durability, efficiency, and effective illumination. Here are its main components:
1. The Mast
The mast is the tall, vertical structure that elevates the lights. Made from high-strength steel or aluminum, it must be strong enough to support the weight of the light fixtures while withstanding wind, rain, snow, and other environmental conditions. Masts are often tapered (wider at the base, narrower at the top) to improve stability and reduce wind resistance. They may also include a ladder or access platform for emergency maintenance, though most modern high mast light systems rely on lowering mechanisms instead.
2. Light Fixtures
Mounted at the top of the mast, the light fixtures are the core of the high mast light system. A single high mast light can have anywhere from 4 to 16 fixtures, depending on the area to be illuminated. Each fixture contains one or more bulbs—most commonly LEDs, which offer several advantages:
- Energy efficiency: LEDs use up to 75% less energy than traditional bulbs.
- Long lifespan: LED bulbs can last 50,000–100,000 hours, reducing maintenance needs.
- Directional lighting: LEDs can be designed to focus light exactly where it’s needed, reducing waste and light pollution.
- Instant illumination: Unlike some traditional bulbs, LEDs light up immediately without warm-up time.
The fixtures are arranged in a circular or rectangular pattern to ensure even light distribution across the target area.

3. Lowering Mechanism
One of the defining features of a modern high mast light system is its lowering mechanism. This system allows the entire light fixture assembly to be safely lowered to ground level for maintenance, rather than requiring workers to climb the mast or use expensive lifting equipment. Common lowering mechanisms include:
- Winch systems: A motorized winch with cables that raise and lower the light assembly.
- Hydraulic systems: Hydraulic cylinders that smoothly lift and lower the fixtures.
- Manual systems: Hand-cranked mechanisms for smaller high mast light installations.
This feature significantly reduces maintenance costs and improves safety for workers.
4. Foundation and Base
To support the tall mast and withstand environmental forces, a high mast light requires a strong foundation. This typically consists of a large concrete base, often buried several feet underground, with anchor bolts that secure the mast to the foundation. The base must be engineered to handle the mast’s weight, wind loads, and any potential ice or snow accumulation. In areas prone to high winds or earthquakes, the foundation may be reinforced with additional steel or deeper concrete footings.
5. Control System
Modern high mast light systems often include smart control systems to optimize operation. These can include:
- Photocells: Sensors that automatically turn the high mast light on at dusk and off at dawn.
- Timers: Programmable controls to adjust lighting schedules based on specific needs.
- Dimming capabilities: The ability to reduce light output during low-traffic hours to save energy.
- Remote monitoring: Systems that allow operators to check the status of the high mast light, detect faults, and control lighting remotely via computer or mobile device.
How Does a High Mast Light Work?
A high mast light works by elevating powerful light sources to a great height, allowing their illumination to spread over a large area. The key to its effectiveness lies in its height and the design of its light distribution:
- Elevation advantage: By placing lights 60–150 feet above the ground, a high mast light can cover an area with a radius of 300–500 feet or more. This is far greater than the coverage of a standard 20-foot-tall streetlight, which might only cover a 50–100-foot radius.
- Light distribution design: The fixtures are angled and spaced to ensure the light overlaps evenly across the target area, eliminating dark spots. This is especially important for safety in areas like highways or airports, where uneven lighting could create hazards.
- Controlled intensity: High mast light systems are engineered to provide the right level of brightness for their specific application. For example, highway interchanges may require brighter lighting than parking lots, while sports stadiums need precise lighting levels to meet broadcast standards.
When activated, the bulbs in the fixtures emit light that is directed downward and outward, creating a large pool of illumination. The control system ensures the high mast light operates only when needed, conserving energy and reducing light pollution.
Where Is a High Mast Light Used?
High mast lights are used in any large area that requires bright, uniform lighting during nighttime hours. Their ability to cover vast spaces with fewer poles makes them both cost-effective and space-efficient. Here are the most common applications:
Highways and Transportation Hubs
One of the most widespread uses of high mast lights is along highways, interchanges, and toll plazas. These areas require consistent lighting to ensure driver safety, especially in locations with complex traffic patterns, exits, or merges. A high mast light can illuminate an entire interchange from a single position, reducing the need for multiple shorter poles that could clutter the landscape or distract drivers.
High mast lights are also used in:
- Truck stops and rest areas: Providing bright lighting for large parking areas where commercial vehicles stop overnight.
- Rail yards: Illuminating large rail facilities to ensure safe operations during night shifts.
- Bus terminals: Lighting bus depots and parking areas for passenger safety and operational efficiency.
Ports and Airports
Ports, harbors, and airports are vast facilities that operate 24 hours a day, requiring reliable lighting for loading/unloading operations, aircraft movement, and safety. High mast lights are ideal for these environments because:
- They can illuminate large cargo yards, container storage areas, and runway aprons.
- Their tall height avoids interference with cranes, ships, or aircraft.
- They provide uniform lighting essential for precision operations, such as loading containers or guiding aircraft to gates.
In airports, high mast lights are often used in parking lots, maintenance areas, and around runways (though runway lighting itself uses specialized fixtures). In ports, they light up docks, storage yards, and navigation areas.
Industrial Facilities and Factories
Industrial complexes, manufacturing plants, and factories often have large outdoor areas that need lighting for nighttime operations, security, and safety. High mast lights are used to illuminate:
- Storage yards: Where raw materials, equipment, or finished products are stored outdoors.
- Loading docks: Ensuring safe loading and unloading of goods during night shifts.
- Factory perimeters: Enhancing security by lighting fences and access points.
- Construction sites: Temporary high mast light installations provide illumination for nighttime construction work, especially on large projects like bridges or highways.
Industrial high mast lights are often ruggedized to withstand harsh conditions, such as exposure to chemicals, dust, or heavy machinery vibrations.
Sports Facilities and Stadiums
Sports stadiums, athletic fields, and recreation complexes require high-quality lighting for evening and night events. High mast lights are commonly used in:
- Outdoor stadiums: For football, soccer, baseball, and track events, where the entire playing field and spectator areas need bright, uniform lighting.
- Golf courses: Lighting driving ranges or practice areas for night use.
- Public parks and recreation areas: Illuminating large sports fields, skate parks, or multi-use trails.
In sports applications, high mast lights must meet specific standards for light intensity, uniformity, and color temperature to ensure visibility for players, spectators, and television broadcasts. LED high mast lights are particularly popular here because they can be tuned to the optimal color temperature for sports visibility.
Parking Lots and Transportation Centers
Large parking lots at shopping malls, airports, universities, and business parks benefit greatly from high mast lights. A single high mast light can illuminate an entire parking lot, providing several advantages:
- Improved safety: Bright, uniform lighting reduces shadows where criminal activity could occur and helps drivers and pedestrians navigate safely.
- Reduced pole clutter: Fewer poles mean more open space for parking and easier navigation.
- Cost efficiency: Lighting a large lot with a few high mast lights is often cheaper than installing dozens of shorter poles.
Bus terminals, train stations, and subway parking areas also rely on high mast lights to ensure passenger safety during early morning or late-night hours.
Mining and Quarry Operations
Mining sites, quarries, and other extractive operations are typically large, remote areas that operate around the clock. High mast lights are essential here for:
- Illuminating mining pits, loading areas, and haul roads.
- Ensuring safety for workers operating heavy machinery in low-light conditions.
- Supporting security by lighting site perimeters.
Mining high mast lights are built to withstand extreme conditions, including dust, vibration, and temperature extremes. They often have protective housings to shield bulbs from debris.
Public Spaces and Events
In some cases, high mast lights are used in public spaces for special events or temporary needs:
- Festival grounds: Providing lighting for large outdoor events, concerts, or fairs.
- Emergency situations: Temporary high mast lights can be deployed after natural disasters to illuminate disaster areas, aid in rescue efforts, or provide light for temporary shelters.
- Construction zones: Portable high mast lights are used to light road construction areas, allowing work to proceed safely at night with minimal disruption to traffic.
Benefits of Using a High Mast Light
The popularity of high mast lights stems from their numerous advantages over traditional lighting systems:
- Wide coverage: A single high mast light can illuminate an area that would require dozens of standard streetlights, reducing infrastructure needs.
- Uniform lighting: The elevated position ensures light is evenly distributed, eliminating dark spots that can create safety hazards.
- Energy efficiency: Modern LED high mast lights use significantly less energy than traditional lighting systems, reducing operational costs.
- Lower maintenance: LED bulbs last much longer than traditional bulbs, and the lowering mechanism makes maintenance safer and cheaper.
- Reduced clutter: Fewer poles mean less visual obstruction and more usable space in the illuminated area.
- Improved safety: Bright, uniform lighting enhances visibility for drivers, workers, and pedestrians, reducing accidents and criminal activity.
- Flexibility: High mast lights can be customized with different numbers of fixtures, bulb types, and control systems to meet specific needs.
FAQ
How tall is a typical high mast light?
Most high mast lights range from 60 feet (18 meters) to 150 feet (45 meters) in height. The exact height depends on the area to be illuminated—larger areas require taller masts.
What type of bulbs are used in high mast lights?
Modern high mast lights primarily use LED bulbs, which offer energy efficiency, long lifespans, and good light quality. Older systems may use metal halide or high-pressure sodium bulbs, but these are being phased out in favor of LEDs.
How much area can a high mast light cover?
A single high mast light can typically illuminate an area with a radius of 300–500 feet (90–150 meters), depending on its height, the number of fixtures, and the bulb wattage.
How often do high mast lights require maintenance?
With LED bulbs, high mast lights need bulb replacements every 5–10 years. Other maintenance, such as cleaning fixtures or inspecting the lowering mechanism, is usually required annually.
Are high mast lights energy efficient?
Yes, especially modern LED high mast lights. They use significantly less energy than traditional lighting systems, and many include dimming or smart controls to further reduce energy use during low-demand periods.
Can high mast lights withstand severe weather?
Yes. High mast lights are engineered to withstand high winds, heavy rain, snow, and ice. Their foundations are reinforced, and masts are made from strong materials like steel to ensure stability.
Are high mast lights expensive to install?
The initial installation cost is higher than for standard lighting, due to the tall mast and foundation. However, over time, they are often more cost-effective because they require fewer poles, use less energy, and have lower maintenance costs.
Table of Contents
- What Is a High Mast Light?
- Key Components of a High Mast Light System
- How Does a High Mast Light Work?
- Where Is a High Mast Light Used?
- Benefits of Using a High Mast Light
-
FAQ
- How tall is a typical high mast light?
- What type of bulbs are used in high mast lights?
- How much area can a high mast light cover?
- How often do high mast lights require maintenance?
- Are high mast lights energy efficient?
- Can high mast lights withstand severe weather?
- Are high mast lights expensive to install?